
Roofing
Injuries from falls and other sources can be prevented with proper precautions, equipment and training. Many sections of the occupational health and safety regulations are relevant to working on a roof and roofing activities. Be sure to view other summaries, especially fall protection, to get all the information you may need.
While work activities on roofs may result in falls, it is important to note that there are other hazards as well, including:
- Equipment such as scaffolding or ladders not set up or used properly.
- Exposure to prolonged cold or hot temperatures, or when you stand up after working in an awkward position for a long time your brain “tricks” you and you feel like you are moving.
- Working with propane.
- Material handling.
- Working near electrical lines.
- Lack of or improper use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and, in particular, fall arresting or travel restraint equipment.
- Improper post-fall rescue procedures.
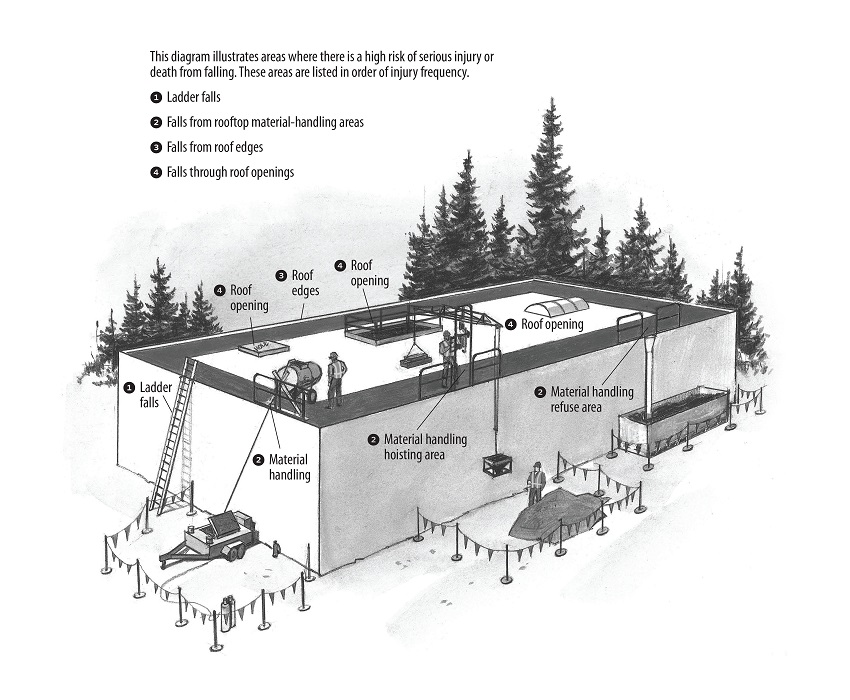
The regulatory requirements and your responsibility as an employer depend on the type of work being carried out. For example, roof work can include weatherproofing as well as preparatory work (such as removing existing material and roof repair), snow removal and roof inspections.
When weatherproofing, as an employer you must ensure:
- Your employees use all the personal protective equipment you are required to provide, including hard hats, safety footwear, eye protection and a fall protection system.
- A fall protection code of practice is written if you choose to use a safety monitor and work procedures, or if you are working from a height of 7.5 metres or more.
- That a warning line is used if a safety monitor is part of your fall protection system.
- Adequate safety precautions are taken if the warning line is 1 m from an unguarded edge.
- Employees working in the control zone use another method of fall protection in addition to the warning line
- That no employees enter the control zone unless required.
- If your employees work 3 m or more above the ground or other safe working level and the roof has a slope exceeding 4 in 12 and the edge is unguarded, that they use a fall arresting system.
The following requirements could apply to both weatherproofing and non-weatherproofing activities, including inspection and repair of roof and removal of old weatherproofing material. As an employer you must ensure:
- The fall protection system used must meet the appropriate standards and regulations.
- If a travel restraint is used as a means of fall protection, it is rigged to prevent employees from reaching an unguarded edge and that it has the following requirements.
- That hoists used to raise materials to the roof are strong and stable, and equipped with suitable ropes, chains, slings, hooks and other fittings.
- That weights used to counterbalance a hoist are adequate and secured.
- Guardrails or a safety fence (that are manufactured as part of the hoist) are installed in the perimeter travel areas on a roof near the hoist and dumping areas.
While the employer is ultimately responsible for all the provisions mentioned above, the supervisor has a vital role to play in the safety of their teams. As a supervisor, you must:
- Acquaint your employees with the hazards and control measures associated with their work
- Provide the information and instruction necessary to ensure their health and safety
- Enforce company safety rules, programs, codes of practice and procedures, including ensuring employees comply with the requirements below.
As an employee, you must:
- Follow the training provided by your employer.
- Follow the instruction provided by your employer or supervisor.
- Not enter a control zone unless required for your work.
- Use the personal protective equipment provided by your employer including hard hats, safety footwear, eye protection and fall protection system.
- Use a fall arrest system when doing weatherproofing work that is 3 m or more above ground (or above a safe working level), has a slope that is more than 4 in 12, and has an unguarded edge.
“weatherproofing” is the application of tar, asphalt, gravel, insulation, shingles or membrane material to a roof but does not include the installation of decking materials or the stripping of materials from the roof.
50.2(4) The code of practice shall include the following:
(a) possible hazardous situations, including a description of the hazards and the possible effects on the health or safety of employees;
(b) the identification of employees at risk;
(c) the location where the code of practice might apply;
(d) the methods and equipment to be used including inspections procedures;
(e) the procedures and equipment which might be required in the event of an emergency;
(f) the times, days, or events during which the code of practice might be applicable;
(g) the identification of training needs;
(h) the identification of the person responsible for implementing the code of practice; and
(i) the name of the safety monitor, if applicable, and the training the safety monitor has received
The safety monitor shall:
- Be experienced in the work overseen and trained to be a safety monitor.
- Be present at all times when an employee is in the control zone.
- Have authority over the work to prevent falls.
- Have a clear view of the work being done.
- Be able to communicate without needing to yell.
- Be instantly distinguished from other workers.
- Do no other duties while acting as safety monitor.
- Monitor no more than eight workers.
“warning line” means a supported raised line marking the edge of a control zone;
“adequate” means sufficient to protect a person from the risk of injury or damage to health
“control zone” means the area between an unguarded edge and a warning line which represents a safe distance from the edge.
When employees are engaged in weatherproofing, a safety monitor may be used as the means of fall protection. Other means of fall protection include travel restraint, fall arrest or safety nets.
“fall-arresting system” means a permanent or temporary assembly of fall-protection components designed to arrest the fall of one or more employees.
Is attached to an anchor point that will support two times the maximum load, and when used on a roof with a slope greater than 3 in 12, is attached to an anchor point that will withstand a 22kN force (or 4 times the maximum load when used under the direction of a competent person).
OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY ACT
S.N.B. 1983, c. O-0.2
DUTIES OF EMPLOYERS, OWNERS, CONTRACTORS, SUB-CONTRACTORS, SUPERVISORS, EMPLOYEES AND SUPPLIERS
Section 9 Duties of employer
9. (1) Every employer shall
(a) take every reasonable precaution to ensure the health and safety of its employees;
(b) comply with this Act, the regulations and any order made in accordance with this Act or the regulations; and
(c) ensure that its employees comply with this Act, the regulations and any order made in accordance with this Act or the regulations.
(2) Without limiting the generality of the duties under subsection (1), every employer shall
(a) ensure that the necessary systems of work, tools, equipment, machines, devices and materials are maintained in good condition and are of minimum risk to health and safety when used as directed by the supplier or in accordance with the directions supplied by the supplier;
(a.1) ensure that the place of employment is inspected at least once a month to identify any risks to the health and safety of its employees;
(b) acquaint an employee with any hazard in connection with the use, handling, storage, disposal and transport of any tool, equipment, machine, device or biological, chemical or physical agent;
(c) provide the information that is necessary to ensure an employee’s health and safety;
(c.1) provide the instruction that is necessary to ensure an employee’s health and safety;
(c.2) provide the training that is necessary to ensure an employee’s health and safety;
(c.3) ensure that work at the place of employment is competently supervised and that supervisors have sufficient knowledge of all of the following with respect to matters that are within the scope of the supervisor’s duties:
(i) this Act and any regulations under this Act that apply to the place of employment;
(ii) any safety policy for the place of employment;
(iii) any health and safety program for the place of employment;
(iv) any health and safety procedures with respect to hazards in connection with the use, handling, storage, disposal and transport of any tool, equipment, machine, device or biological, chemical or physical agent by employees who work under the supervisor’s supervision and direction;
(v) any protective equipment required to ensure the health and safety of the employees who work under the supervisor’s supervision and direction; and
(vi) any other matters that are necessary to ensure the health and safety of the employees who work under the supervisor’s supervision and direction;
(c.4) ensure that work at the place of employment is sufficiently supervised;
(d) provide and maintain in good condition such protective equipment as is required by regulation and ensure that such equipment is used by an employee in the course of work;
(e) co-operate with a committee, where such a committee has been established, a health and safety representative, where such a representative has been elected or designated, and with any person responsible for the enforcement of this Act and the regulations.
(3) An employer shall develop a program for the inspection referred to in paragraph (2)(a.1) with the joint health and safety committee, if any, or the health and safety representative, if any, and shall share the results of each inspection with the committee or the health and safety representative.
[S.N.B. 2001, c. 35, s. 3; 2007, c. 12, s. 2; 2013, c. 15, s. 4; 2019, c. 38, s. 4; 2022, c. 32, s. 5]
Section 12 Duties of employee
12. Every employee shall
(a) comply with this Act, the regulations and any order made in accordance with this Act or the regulations;
(b) conduct themselves to ensure their own health and safety and that of other persons at, in or near the employee’s place of employment;
(c) report to the employer or supervisor the existence of any hazard of which the employee is aware;
(d) wear or use such protective equipment as is required by regulation;
(e) consult and co-operate with the committee where one has been established or with the health and safety representative where one has been elected or designated; and
(f) co-operate with any person responsible for the enforcement of this Act and the regulations.
[S.N.B. 2001, c. 35, s. 6; 2007, c. 12, s. 3; 2019, c. 38, s. 7; 2022, c. 32, s. 7]
General Regulation - Occupational Health and Safety Act
N.B. Reg. 91-191
Part VII PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT
Section 38 General
38. (1) Where protective equipment is required to be used by an employee under this Regulation, an employer shall ensure that the employee is instructed and trained on how to use, care for and inspect the protective equipment in accordance with the manufacturer’s specifications.
(2) Where protective equipment is required to be used by an employee under this Regulation, an employee shall
(a) use the equipment that is required in accordance with the instruction and training received,
(b) test or visually inspect the equipment before each use as appropriate to the type of equipment to be used,
(c) report any defective equipment to the employer and not use the equipment, and
(d) care for the equipment properly while using it.
[N.B. Reg. 2024-38, s. 23]
Section 49.1
49.1(1) An owner of a place of employment, an employer and a contractor shall each ensure that the components of a fall-protection system
(a) are designed in accordance with good engineering practices,
(b) are erected, installed, assembled, used, handled, stored, adjusted, maintained, repaired and dismantled in accordance with the manufacturer's specifications, and
(c) meet the requirements of the applicable standards.
(2) For the purposes of paragraph (1)(c), the following CSA standards apply:
(a) Z259.1-05 , "Body Belts and Saddles for Work Positioning and Travel Restraint" or Z259.1-95 , "Safety Belts and Lanyards";
(b) Z259.2.4:15 (R2020), "Fall arresters and vertical rigid rails" , or a standard offering equivalent or better protection;
(b.1) Z259.2.5-17, "Fall arresters and vertical lifelines" , or a standard offering equivalent or better protection;
(c) Z259.2.2-17 (R2022), "Self-retracting devices" , or a standard offering equivalent or better protection;
(d) Z259.2.3-99 , "Descent Control Devices", or a standard offering equivalent or better protection;
(e) Z259.10-18, "Full body harnesses" , or a standard offering equivalent or better protection;
(f) Z259.11-17, "Personal energy absorbers and lanyards" , or a standard offering equivalent or better protection;
(g) Z259.12-16 (R2021), "Connecting components for personal fall-arrest systems (PFAS)" , or a standard offering equivalent or better protection;
(h) Z259.14-01 , "Fall Restricting Equipment for Wood Pole Climbing", or a standard offering equivalent or better protection;
(i) Z259.13-04 , "Flexible Horizontal Life Line Systems";
(i.1) Z259.15-12 (R2016), Anchorage connector , or a standard offering equivalent or better protection; and
[N.B. Reg. 2010-159, s. 5; 2022-76, s. 1; 2024-38, s. 31]
Section 50.2
50.2 (1) An employer and a contractor shall each ensure that a fall-protection code of practice is written for a place of employment if a fall-protection system is required for the place of employment and
(a) the employees are working from a height of 7.5 m or more,
(a.1) the employees are performing rope access work other than rope access work for emergency rescue purposes,
(b) the employer uses a safety monitor and work procedures when weatherproofing as the means of fall-protection, or
(c) an officer requires that the code of practice be written.
(2) The code of practice must be readily available at the place of employment before work begins and employees must have received instruction with regards to the code of practice.
(3) The code of practice shall be developed in consultation with the committee or the health and safety representative, if any, or with the affected employees.
(4) The code of practice shall include the following information:
(a) possible hazardous situations, including a description of the hazards and the possible effects on the health or safety of employees;
(b) the identification of employees at risk;
(c) the location where the code of practice might apply;
(d) the methods and equipment to be used including inspections procedures;
(e) the procedures and equipment which might be required in the event of an emergency;
(f) the times, days, or events during which the code of practice might be applicable;
(g) the identification of training needs;
(h) the identification of the person responsible for implementing the code of practice; and
(i) the name of the safety monitor, if applicable, and the training the safety monitor has received.
[N.B. Reg. 2010-159, s. 7; 2022-27, s. 25; 2024-38, s. 32]
Part X CONSTRUCTION, TRAFFIC AND BUILDING SAFETY
Section 105 Roofs
105. (1) An employer and a contractor shall each ensure that a warning line is
(a) not less than 2 m from the unguarded edge,
(b) has a minimum diameter of 10 mm,
(c) is suspended at a height of not less than 750 mm and not more than 900 mm,
(d) is supported by corner and intermediate posts sufficient to keep the line taut, and
(e) has readily visible markers placed every 1.5 m along the length of the line.
(2) Despite paragraph (1)(a), a warning line may be 1 m from an unguarded edge at the dump point for snow removal or when an employee is engaged in weatherproofing, provided adequate precautions are taken to ensure the safety of the employee.
(3) An employer shall ensure that an employee who is working in the control zone uses another method of fall-protection in addition to the warning line.
(4) When employees are engaged in weatherproofing, a safety monitor may be used as the means of fall-protection for employees working in the control zone.
(5) The safety monitor referred to in subsection (4) shall ensure that tasks being performed in the control zone are performed in accordance with the fall-protection code of practice and in a manner that minimizes the potential for an employee to fall.
(6) A safety monitor referred in subsection (4) shall
(a) be experienced in the work overseen and trained in the role of safety monitor,
(b) be present at all times when an employee is in the control zone,
(c) have complete authority over the work as it relates to the prevention of falls,
(d) be located so as to have a clear view of the work being performed by the employee,
(e) be able to communicate with the employees being protected without needing to yell,
(f) be instantly distinguishable from other workers,
(g) engage in no other duties while acting as the safety monitor, and
(h) monitor a maximum of eight workers.
(7) An employer shall ensure that no employee enters the control zone unless the employee is required to do so by reason of the employee's work duties.
(8) The owner of a place of employment, employer and contractor shall each ensure a travel restraint system
(a) is rigged to prevent the employee from reaching an unguarded edge,
(b) is, subject to paragraph (c), attached to an anchor point capable of supporting two times the maximum load likely to be applied to it, or
(c) when it is used on a roof with a slope greater than 3 in 12, is attached to an anchor point that is capable of withstanding a 22 kN force or, if used under the direction of a competent person, four times the maximum load that may be generated in the fall-arresting system.
[N.B. Reg. 96-60, s. 1; 2010-159, s. 18]
Section 106
106. An employer shall ensure that an employee who is engaged in the weatherproofing of a roof that
(a) is 3 m or more above the ground or other safe working level,
(b) has a slope exceeding 3 in 12, and
(c) has an unguarded edge,
uses an individual fall-arresting system and the employee shall use the individual fall-arresting system.
[N.B. Reg. 96-60, s. 2; 2024, c. 5, s. 2]
Section 109 Hoisting apparatus used to raise materials to roof
109. (1) Repealed. [N.B. Reg. 2022-79, s. 16]
(2) An employer shall ensure that the weights used to counterbalance a hoisting apparatus used to raise materials to a roof are
(a) adequate for the equipment used, and
(b) secured to the hoisting apparatus to prevent their premature removal.
[N.B. Reg. 2022-79, ss. 16, 17]
Section 110 Hoisting apparatus used to raise materials to roof
110. An employer shall ensure that guardrails, or a safety fence manufactured as part of a hoisting apparatus, are installed in perimeter travel areas on a roof near the hoist areas and the dumping areas.
[N.B. Reg. 96-60, s. 6; 2022-79, ss. 18, 19]
Openings