
Scaffolding
Although scaffolding can provide an efficient and safe means of performing work, many incidents happen because scaffolds are improperly used or installed. Falls from improperly constructed or used scaffolds can result in injuries ranging from sprains to death.
Scaffolding consists of a temporary elevated platform that is used to support materials and employees while they work at heights. In most cases, scaffolding can be equipped with guardrails at any edge that exposes an employee to heights.
Different types of scaffolds are:
Wood Scaffolds - A supported scaffold consisting of a platform supported by brackets attached to a building or structural walls.

Horse Scaffolds - A supported scaffold consisting of a platform supported by construction horses (sawhorses). Horse scaffolds made of metal are also called trestle scaffolds.

Ladder Jack Scaffolds - A supported scaffold consisting of a platform resting on brackets attached to ladders.

Pump-jack Scaffolds - A supported scaffold consisting of a platform supported by vertical poles and movable support brackets.

Mobile Rolling Scaffolds - A portable caster or wheel-mounted supported scaffold.
Frame Scaffolds - Popular and widely used scaffolds because of the simplicity of design, speed at which they can be erected, component availability, portability, and ease of use. They can range from light duty to extra heavy duty depending on the size and spacing of the components.
Tube and Clamp Systems - Consist of various lengths of steel or aluminium tubing being connected with rigid clamps where vertical and horizontal members intersect, and swivel clamps where diagonal members are used.
Hazards associated with scaffolding are:
- Access
- Collapse
- Failure of guardrails, planks and platforms
- Electrical
- Falls
- Falling objects/items
- Instability
Proper preplanning and appropriate controls help make sure the scaffold is erected safely and used properly. These controls include:
- Choosing the type of scaffold appropriate for the job.
- Determining the maximum load of the scaffold.
- Assuring a good foundation.
- Avoiding electrical hazards.
- Inspecting all components of a metal scaffold or wood scaffold for defects.
- If using a manufactured scaffold, ensuring it is erected, used, maintained, and dismantled in accordance with the manufacturer's specifications.
- If over 3 m in height , or a mobile rolling scaffold , installing guardrail systems along all open sides and ends of platforms.
- Providing safe access to scaffold platforms.
- If using a metal scaffold, access must be provided from ground level. If less than 6 m in height, providing a continuous access ladder or stairway. If 6 m or more in height, providing a continuous access stairway. If it is not possible to install a continuous access stairway, equip with a ladder.
- Making sure no one climbs cross-bracing as a means of access.
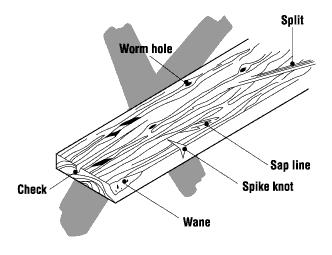
It is important to know how to identify defects in planks. Common defects of scaffold planks are:
- Checks - Lengthwise crack or separation occurring across annual rings. No such splits or cracks are permitted within three inches from the edge of the plank, and planks with splits wider than 10 mm (3/8”) must be removed from use.
- Shakes - Lengthwise separations along the grain, the greater part of which occurs between the annual rings.
- Wane - The bark or lack of wood on the face of a plank.
- Knots: Must be sound, tight, and well-spaced. The maximum allowable size for the wide face of a 2” x 10” plank is 50 mm or 1 7/8”. For 2” x 12” planks the maximum is 60 mm or 2 3/8”. On the edges there should be no knots larger than 10 mm or 3/8” in the middle third of the plank. Planks with spike knots should be rejected.
As an employer, you must:
- Ensure that a scaffold
- Can sustain a minimum uniformly distributed load of 1.4kPa.
- Can support at least four times the load that may be used on it.
- That is over 3 m, has a guardrail that meets the requirements of Section 97 , or if a mobile rolling scaffold, has guardrails regardless of the height.
- Has lockable wheels if it is a mobile rolling scaffold.
- Is erected plumb and level.
- Has vertical supports resting on a firm foundation or sills.
- Is secured to prevent lateral movement.
- Has a platform that is at least 500 mm wide
- If a mobile rolling scaffold, has a solid platform covering the entire area from which an employee may work.
- If it uses manufactured planks, has a platform that is at least 450 mm wide.
- Make sure that the brackets of a bracket scaffold are not more than 3 metres apart and are securely attached so they do not dislodge.
- Make sure a bracket scaffold is erected, installed, assembled, started, operated, used, handled, stored, stopped, serviced, tested, cleaned, adjusted, maintained, repaired, inspected, and dismantled according to the manufacturer’s specifications, or it is designed by an engineer, according to that design.
- Ensure that when a guardrail is removed that adequate precautions are taken to ensure employee safety and that the area is not left unguarded until the guardrail is reinstalled.
- Ensure spacing of vertical supports and bearers are at intervals not exceeding 3 m for light work and 2.1 m for heavy work (bricklaying, masonry, etc.).
- Ensure that a sawn lumber plank in a scaffold is at least 50 mm thick by 250 mm wide rough sawn lumber, has a span not longer than 3 m, extends at least 150 mm, is laid flat with an overlap of 300 mm and is secured.
- The plank is made of No. 2 grade or better spruce, pine or fir, is not painted (other than being preserved by a transparent protective coating) and is inspected by a competent person before each use.
- Provide safe means of access to all working levels of scaffold.
- Ensure that employees who work below a scaffold are protected from falling objects by overhead protection or by other means such as tying off tools.
- Prohibit the use of ladders to gain greater heights on scaffolds.
- Ensure that materials, snow, ice, etc. that could cause trips and falls are removed.
- Review the sections of legislation pertinent to the type of scaffolding used, and ensure compliance.
While the employer is ultimately responsible for all the provisions mentioned above, the supervisor has a vital role to play in the safety of their teams. As a supervisor, you must:
- Acquaint your employees with the hazards and control measures associated with their work
- Provide the information and instruction necessary to ensure their health and safety
- Enforce company safety rules, programs, codes of practice and procedures, including ensuring employees comply with the requirements below.
As an employee, you must:
- Be trained to inspect, erect and dismantle scaffolding, identify the associated hazards and understand the procedures to control or minimize those hazards.
- Visually inspect the scaffold before each use and report any defects to the employer and not use the scaffold.
- Keep only materials for current use on the scaffold.
- Not move the scaffold with employees or unsecured items on the scaffold.
- Only remove the diagonal supporting brace at the working level to access that level, and only then if other precautions are taken to ensure the scaffold's strength. Ensure the brace is replaced when the work is completed.
- Tie off tools or equipment and handle materials safely to protect the safety of employees below.
- Only use the scaffolding when it is safe (guardrails installed, properly secured, cross-braces installed, safe access and egress, sitting on safe footings, etc.).
- Use scaffolds only when at a safe distance from electrical wires.
- Not work on a scaffold when there are high winds.
General Regulation - Occupational Health and Safety Act
N.B. Reg. 91-191
Part X CONSTRUCTION, TRAFFIC AND BUILDING SAFETY
Section 97 Guardrails
97. (1) A guardrail shall
(a) be made of one of the following materials:
(i) if made of wood,
(A) the top rail, vertical supporting posts and intermediate rail shall be constructed of at least 50 mm × 100 mm No. 2 grade or better SPF, these measures being nominal, and
(B) shall not be painted other than by a transparent protective coating,
(ii) if made of metal pipe,
(A) the top rail and vertical supporting posts shall be at least 40 mm in diameter, and
(B) the intermediate rail shall be at least 25 mm diameter,
(iii) if made of angle iron,
(A) the top rail and vertical supporting posts shall be at least 40 mm × 40 mm by 5 mm, and
(B) the intermediate rail shall be at least 32 mm × 32 mm × 3 mm, or
(iv) if made of wire rope,
(A) the vertical supporting posts shall be made of steel of at least 40 mm in diameter or of a material of equivalent strength, and
(B) the top rail and intermediate rail shall be at least 10 mm in diameter, be attached to a welded fastening on the vertical supporting posts with metal clips to prevent unnecessary sagging and be easily distinguishable from the background; or
(b) be pre-engineered.
(2) A guardrail shall
(a) have a height of not less than 900 mm or more than 1.07 m from the floor level,
(b) have a toeboard which
(i) is at least 127 mm high,
(ii) is fastened to the inside of the vertical supporting posts, and
(iii) has a space of not more than 6 mm between the bottom of the toeboard and the floor,
(c) have vertical supporting posts not more than 2.4 m apart along its entire length unless otherwise specified in manufacturer's specifications, and
(d) have vertical supporting posts not more than 3 m apart along its entire length if the guardrail is used on scaffolding.
(3) The vertical supporting posts referred to in paragraphs 2(c) and (d) shall be adequately fastened to the structure to support the loads imposed upon it.
(4) Unless the guardrail is a pre-engineered guardrail, the top rail shall be fastened to the top or inside of the vertical supporting posts and the intermediate rail shall be fastened to the inside of the vertical supporting posts midway between the top rail and the floor level.
(5) A guardrail shall be made of materials with sufficient strength and rigidity to support loads with the following minimums:
(a) 675 N in any direction, at any point along the top rail;
(b) 450 N in any direction, at any point along the intermediate rail; and
(c) 900 N in any direction, at any point along the top rail, intermediate rail and toeboard if the guardrail is used on a surface that is sloped more than 3 in 12 and less than 6 in 12.
[N.B. Reg. 2001-33, s. 33; 2010-159, s. 14]
98. Repealed. [N.B. Reg. 2010-159, s. 15]
Section 100
100. (1) Where a guardrail is removed in order for work to be done, an employer and a contractor shall each ensure that
(a) adequate precautions are taken to ensure the safety of the employee doing the work and any other employee, and
(b) the area is not left unguarded.
(2) An employee who removes a guardrail in order to do work shall replace the guardrail before leaving the area.
Part XI TEMPORARY STRUCTURES
Section 131 General Provisions Applicable to Scaffolds
131. (1) An employer and a contractor shall each ensure that a scaffold
(a) is capable of sustaining a minimum uniformly distributed load of 1.4 kPa,
(b) is at no time subjected to a load that exceeds the equivalent of one-quarter of the load for which it is designed,
(c) is designed and constructed to support at least four times the load that may be imposed on it,
(d) if 3 m or more in height, has a guardrail that meets the requirements of section 97,
(e) is erected plumb and level,
(f) has vertical supports resting upon a firm foundation or sills,
(g) is adequately secured at vertical intervals not exceeding three times the least lateral dimension of the scaffold, measured at the base, to prevent lateral movement,
(h) if sawn lumber planks are used as a platform, has a platform that is at least 500 mm wide, and
(i) if using manufactured scaffold planks, has a platform that is at least 450 mm wide.
(2) Paragraph (1)(d) does not apply to a mobile rolling scaffold.
(3) Subject to subsection (4), an employer shall ensure that the spacing of vertical supports and bearers of a scaffold does not exceed 3 m on centres.
(4) Where a scaffold is to be used for bricklaying, masonry or other heavy work, an employer shall ensure that the spacing of vertical supports and bearers of a scaffold does not exceed 2.1 m on centres.
[N.B. Reg. 2001-33, ss. 42, 43; 2010-159, s. 27; 2024-38, s. 68]
Section 131.1 Scaffolds - employee requirements
131.1 An employee who uses a scaffold shall
(a) visually inspect the scaffold before each use, and
(b) report to the employer any situation or condition that may make the scaffold unsafe to use and, if nec‐ essary, not use the scaffold.
[N.B. Reg. 2024-38, s. 69]
Section 132 Sawn lumber planks
132. An employer and a contractor shall each ensure that a sawn lumber plank in a scaffold
(a) is at least 50 mm thick by 250 mm wide rough sawn lumber,
(a.1) is made of No. 2 grade or better spruce, pine or fir,
(a.2) is not painted other than by being preserved with a transparent protective coating,
(a.3) is inspected by a competent person before each use to determine the integrity of the plank,
(b) has a span not longer than 3 m,
(c) extends at least 150 mm and not more than 300 mm beyond a supporting member,
(d) is laid flat with an overlap of 300 mm with another plank, with the centre of the overlap directly over a bearer, and
(e) is secured to prevent movement in any direction that may create a danger to an employee.
[N.B. Reg. 2024-38, ss. 70, 71]
Section 133
133. (1) An employer shall ensure that
(a) lean-to scaffolds on wall brackets are not used,
(b) the inner supports of the supporting members on a single pole scaffold are of adequate construction and securely fastened to a wall,
(c) a safe means of access is provided to all working levels of a scaffold, and
(d) no person uses cross-bracing or diagonal bracing on a scaffold for climbing.
(2) Where an employee is working on a scaffold above another employee, the employee working above shall ensure that the employee below is protected from the hazard of objects falling from the higher level by overhead protection or by such means as tying off tools and other unsecured objects on the higher level.
Section 134
134. An employee who works on a scaffold and an employer shall each ensure that
(a) only materials for current use are kept on the scaffold,
(b) the scaffold is not moved with employees or unsecured tools, materials or equipment on the scaffold, and
(c) a diagonal supporting brace is removed at the working face level only for access and only if precautions are taken to ensure that the strength of the scaffold is not weakened and the brace is replaced after the work is completed.
Section 135 Wood Scaffolds
135. (1) An employer shall ensure that the wooden vertical supports of a wood scaffold
(a) when 6 m or less in height, are not less than 50 mm thick by 100 mm wide, and
(b) when greater than 6 m in height, are not less than
(i) 100 mm thick by 100 mm wide, or
(ii) two 50 mm thick by 125 mm wide pieces laminated together.
(2) An employer shall ensure that single wooden vertical supports of a wood scaffold are extended by means of a butt joint that has been strengthened by four pieces of material at least 25 mm thick and of the same width as the vertical supports and extending at least 740 mm on both sides of the butt joint.
(3) An employer shall ensure that the distance between the joints of laminated vertical supports of a wood scaffold is not less than 1.2 m.
(4) An employer shall ensure that the minimum size of a bearer on a wood scaffold is 50 mm thick by 125 mm wide.
[N.B. Reg. 2001-33, s. 44]
Section 136 Metal Scaffolds
136. (1) An employer shall ensure that a metal scaffold
(a) is erected, used, maintained and dismantled in accordance with the manufacturer's specifications,
(b) if less than 6 m in height, is equipped with a continuous access ladder or stairway commencing at ground level, and
(c) if 6 m or greater in height, is equipped with a continuous access stairway commencing at ground level or, if the circumstances do not permit for the metal scaffold to be equipped with a continuous access stairway, with a continuous access ladder commencing at ground level.
(2) An employer shall ensure that
(a) a metal scaffold is regularly inspected for any damage, deterioration or loosening of the connections of its structural members that may affect its strength and if such damage, deterioration or loosening is found, that the scaffold is removed from use until repaired,
(b) cross-bracing and diagonal bracing is installed at each level of a metal scaffold as the erection of the scaffold progresses, and
(c) no person works on a metal scaffold before the cross-bracing and diagonal bracing is in place, except to erect the scaffold.
[N.B. Reg. 2001-33, ss. 45, 46; 2024-38, s. 73]
Section 137 Horse Scaffolds
137. (1) Where the horses for a horse scaffold are constructed of wood, an employer shall ensure that
(a) the horizontal members of bearers are not smaller than 50 mm thick by 125 mm wide,
(b) the legs are not smaller than 50 mm thick by 100 mm wide,
(c) the longitudinal braces between legs are not smaller than 25 mm thick by 150 mm wide,
(d) the gusset braces at the top of the legs are not smaller than 25 mm thick by 200 mm wide, and
(e) the half diagonal braces are not smaller than 25 mm thick by 100 mm wide.
(2) An employer shall ensure that the horses for a horse scaffold are
(a) placed on a secure footing and not raised in height by blocking or extensions,
(b) spaced not more than
(i) 1.5 m apart for a scaffold supporting 3.6 kPa or more,
(ii) 2.3 m apart for a scaffold supporting 1.2 kPa to 3.5 kPa, and
(iii) 3 m apart for a scaffold supporting less than 1.2 kPa, and
(c) placed directly over one another and, if more than two tiers high, each tier is secured to a building or structure.
(3) An employer shall ensure that a platform of a horse scaffold
(a) if supported by single tier horses, does not exceed 5 m in height,
(b) if supported by tiered horses, does not exceed three tiers or 3.7 m in height, whichever is the lower, and
(c) is secured to the legs of the horses to prevent movement.
[N.B. Reg. 2001-33, s. 47]
Section 138 Ladderjack Scaffolds
138. (1) An employer shall ensure that a ladder-jack scaffold
(a) is not more than 5 m in height,
(b) has supporting ladders properly secured against displacement,
(c) is used only for operations where the work period between changes of scaffold position is of short duration and the load on the scaffold does not exceed 1.2 kPa, and
(d) is not used by more than two employees at any one time.
(2) An employer shall ensure that a ladder-jack assembly is securely fastened to the ladder so that it bears on the side rails.
(3) Where a manufactured platform is used on a ladder-jack scaffold, an employer shall ensure that the platform is a minimum of 500 mm in width and is supported at intervals not exceeding 3 m.
[N.B. Reg. 2001-33, ss. 48, 49]
Section 139 Pump-jack Scaffolds
139. An employer shall ensure that a pump-jack scaffold
(a) if made of metal, is not more than 15 m in height and is erected, installed and used according to the manufacturer's specifications, and
(b) if made of wood, is not more than 9 m in height.
[N.B. Reg. 2001-33, s. 50]
Section 140 Mobile Rolling Scaffolds
140. (1) An employer shall ensure that a mobile rolling scaffold
(a) is not higher than four times the width of the smallest base dimension, unless it is guyed or otherwise secured at the top,
(b) has diagonal and horizontal cross-bracing installed at every level,
(c) has a solid platform covering the entire area from which an employee works,
(d) has lockable wheels that are locked while the mobile rolling scaffold is in use, and
(e) has guardrails.
(2) Where a mobile rolling scaffold is equipped with pneumatic tires, an employer and any person who uses the scaffold shall each ensure that the wheels are blocked separately in such a way as to raise the wheels off the ground or floor before the scaffold is used.
(3) An employer and any person who uses a mobile rolling scaffold shall each ensure that the scaffold is not used until inspected before each day's use by a competent person and by the person who is to use the scaffold.
[N.B. Reg. 2001-33, s. 51; 2024-38, s. 74]
Bracket scaffolds
Section 140.01 Bracket scaffold
140.01 (1) An employer shall ensure that the metal brackets of a bracket scaffold are not more than 3 m apart and are securely attached to prevent the brackets from dislodging.
(2) An employer shall ensure that a bracket scaffold is erected, installed, assembled, used, stored, serviced, tested, cleaned, adjusted, maintained, repaired, inspected and dismantled in accordance with the manufacturer’s specifications or, if the scaffold is designed by an engineer, in accordance with the design.
[N.B. Reg. 2024-38, s. 75]
Part XIX ELECTRICAL SAFETY
Section 289 Utility Lines and Utility Line Equipment
289. (1) An employer shall ensure that an employee who is not a qualified person does not carry out any work, and no such employee shall carry out any work, that is liable to bring any person or object closer to an energized electrical utility line or utility line equipment than the distances specified in the following table:
Table
| Phase to Phase Voltage of Energized Electrical Utility Line or Utility Line Equipment | Distance |
| Up to 750 v | 900 mm |
| 750 v - 100,000 v | 3.6 m |
| 100,001 v - 250,000 v | 5.2 m |
| 250,001 v - 345,000 v | 6.1 m |
(2) Where an employee who is not a qualified person is about to commence work that is liable to bring any person or object closer to an energized electrical utility line or utility line equipment than a distance specified in subsection (1), an employer shall contact the authority owning or operating the energized electrical utility line or utility line equipment and shall ensure that the utility line or utility line equipment
(a) is de-energized, or
(b) is adequately insulated or guarded
before permitting the employee to commence the work.
[N.B. Reg. 2001-33, s. 100]