
Traffic Control
Employees who work on roadways, highways, and bridges are exposed to risks from vehicular traffic and machinery. Employees who set up and take down traffic control devices are also at risk.
Traffic cones, barrels, concrete barriers, and trained traffic control persons (signallers) are some of the controls to keep employees safe from vehicular traffic. Controls for traffic on highways and bridges may differ depending on the posted speed, number of lanes, and the type of work being carried out.
Proper signage must always be present and visible in Traffic Control Zones to protect employees, and to advise the motoring public of work being completed on or near the highway. An example of how to set up and take down a Traffic Control Zone is below:
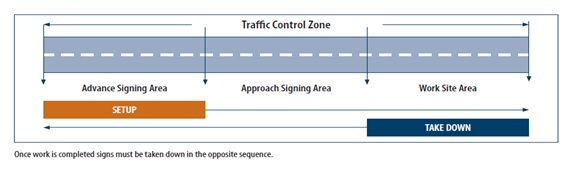
As an employer, you must:
- Establish a safety zone appropriate to the work plan to ensure that work crews don't intrude upon, or conflict with, each other's activities. [Reference: Hazard Alert] While the Work Area Traffic Control Manual (WATCM) developed by the New Brunswick Department of Transportation and Infrastructure (DTI) is not required in regulation, most of the recommended traffic control measures in the manual will not only minimize risk to employees in traffic control situations, but the requirements of the regulations will also be met or exceeded.
- Not assign employees to work in the path of moving equipment. [Reference: Hazard Alert]
- Provide competent traffic control persons (signallers) to control the flow of traffic.
- Provide high-visibility safety apparel that meets the CSA standard Z96-15 (R2020) High-visibility safety apparel or a standard offering equivalent or better protection. This protection must be offered to any employee who may be injured by vehicle traffic, powered mobile equipment, industrial lift trucks, or mobile cranes.
- Erect concrete barriers or material offering equivalent protection at both ends of the construction of a highway or bridge, and as a divider between the traffic and the work area (not required when paving occurs).
- Use appropriate lane control devices and flashing lights or flares.
- Use warning lights or reflective materials to illuminate the materials piled along the sides of any excavation or trench.
- Ensure that the vehicle used to transport the traffic control devices is equipped with high visibility flashing lights.
- Post adequate warning signs in both directions and at any intersection between the warning sign and the work area as indicated:
| Posted Speed (km/hr) |
Distance of Warning Sign from Work Area (m) |
|---|---|
0 - 25 |
25 - 100 |
26 - 50 |
101 - 250 |
51 - 80 |
251 - 500 |
over 80 |
501 - 1,000 |
- Provide adequate barriers around excavations or trenches if there is a hazard potential for the employees from vehicular traffic.
While the employer is ultimately responsible for all the provisions mentioned above, the supervisor has a vital role to play in the safety of their teams. As a supervisor, you must:
- Acquaint your employees with the hazards and control measures associated with their work
- Provide the information and instruction necessary to ensure their health and safety
- Enforce company safety rules, programs, codes of practice and procedures, including ensuring employees comply with the requirements below.
As an employee, you must:
- Wear the high-visibility safety apparel when controlling the flow of traffic, including setting up and taking down traffic control devices.
- Exercise caution at all times, including when setting up and taking down traffic control devices on or near roadways.
- Wear and properly maintain all personal protective equipment.
“competent” means
- (a) qualified, because of such factors as knowledge, training and experience, to do assigned work in a manner that will ensure the health and safety of persons,
- (b) knowledgeable about the provisions of the Act and the regulations that apply to the assigned work, and
- (c) knowledgeable about potential or actual danger to health or safety connected with the assigned work
General Regulation - Occupational Health and Safety Act
N.B. Reg. 91-191
Part X CONSTRUCTION, TRAFFIC AND BUILDING SAFETY
Section 91 Traffic Safety
91. (1) Where construction is being carried out in an area where an employee's safety may be endangered by vehicular traffic, an employer shall provide competent signalers to control the flow of traffic.
(2) An employer shall provide high visibility safety apparel that meets the requirements of CSA standard Z96-15 (R2020), High-visibility safety apparel or a standard offering equivalent or better protection to any employee who is exposed to a risk of injury from vehicular traffic, powered mobile equipment, industrial lift trucks or mobile cranes, and the employee shall wear the apparel.
(3) An employer shall provide and all signalers shall use reflectorized paddles to control the flow of traffic.
[N.B. Reg. 2024-38, s. 56]
Section 92
92. (1) Where construction is being carried out on a highway or bridge and an employee's safety may be endangered by vehicular traffic, an employer shall ensure that
(a) concrete barriers or material offering equivalent protection is erected at both ends of the construction and as a divider between the traffic and the work area of the highway or bridge, and
(b) appropriate lane control devices and flashing lights or flares are used.
(2) Paragraph (1)(a) does not apply where the highway or bridge is being paved.
Section 93
93. (1) Where material is piled along the sides of any excavation or trench and interferes with the flow of vehicular traffic, an employer shall ensure that the material is adequately illuminated by warning lights or reflective materials.
(2) Where work is being carried out and interferes with the flow of vehicular traffic, an employer shall ensure that adequate warning signs are posted in both directions as indicated in the following table and at any intersection between the warning sign and the work area:
Table
| Posted speed (km/hr) | Distance of Warning Sign from Work Area (m) |
| 0 - 25 | 25 - 100 |
| 26 - 50 | 101 - 250 |
| 51 - 80 | 251 - 500 |
| over 80 | 501 - 1,000 |
[N.B. Reg. 2001-33, s. 30]